Multi-modal Learning Pipeline for Smooth Georeferenced Tracking from an Uncalibrated Monocular Camera
Abstract
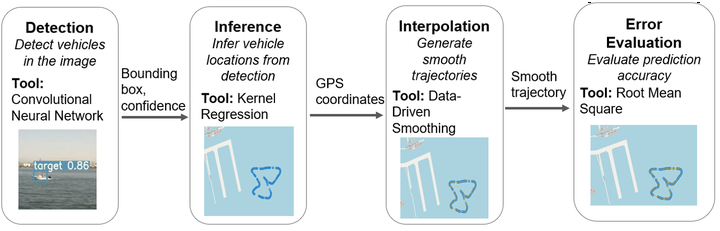
Automatic generation of georeferenced trajectories for vehicular traffic is critical for situational awareness and monitoring for both manned and unmanned platforms, irrespective of their level of autonomy. The goal is to estimate the world coordinates of one or more vehicles from a sequence of images with known camera world coordinates. Traditional depth estimation techniques rely on cues from feature correspondences of multiple viewpoints or knowledge of the camera parameters based on extensive camera calibration. However, camera calibration is a complex and challenging error-prone task. Also, these camera parameters are not guaranteed to be estimable to desired accuracy. This paper presents a lightweight technique to generate georeferenced tracks of vehicular traffic from monocular camera images using a supervised multi-layer model trained on a sparse dataset. The developed pipeline chains well-known highly efficient detection algorithm with novel multi-modal inference learning algorithm, physics-driven interpolation algorithm and an error evaluation process. The novelty of this inference model is the combination of a highly generalizable layer with an extra precision layer, resulting in a highly accurate process with minimal performance degradation across testing and validation datasets. The developed pipeline was tested using real-world maritime traffic images generated from a generic low-cost webcam with, unknown parameters, mounted on a vessel with known GPS coordinates. The whole pipeline was implemented on an NVIDIA Jetson TX2, an embedded system-on-module (SoM) with dual-core NVIDIA Denver2 + quad-core ARM Cortex-A57, 8GB RAM and integrated 256-core Pascal GPU. The results show that the pipeline produces very accurate world coordinate estimates of unseen data using minimal features with unknown camera parameters. The results also show that proposed inference technique is robust to detection uncertainties.