Abstract
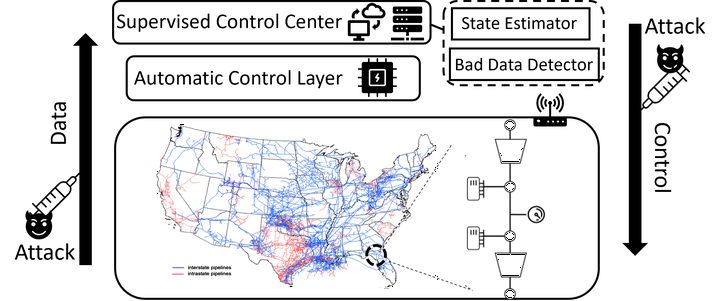
This paper introduces an attack generation framework for evaluating the vulnerability of nonlinear networked pipeline systems. The vulnerability analysis is formulated as determining the presence of feasible attack sets, defined by boundary functions representing the effectiveness and stealthiness of attack signals with respect to the objective and attack detection module. The framework utilizes three data-driven models, including two discriminative models that learn the boundary functions and a generative model that produces elements of the feasible attack set. A new loss function ensures successful attack generation with high probability.
Type
Publication
In 7th IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications 2023